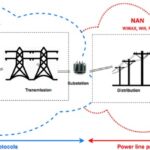
Wireless Sensor Networks:Backbone of Energy Monitoring
In the quest for a more sustainable and energy-efficient future, the role of technology is undeniable. One of the key innovations making waves in this space is Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs). These networks have emerged as the backbone of energy monitoring systems, reshaping how we collect, analyze, and optimize energy usage. In this blog, we’ll delve into the transformative impact of WSNs on energy monitoring and how they contribute to building a greener world.
The Power of Real-Time Data
Unlocking Insights:
Wireless Sensor Networks empower us with real-time data collection capabilities, providing a dynamic view of energy consumption patterns. By continuously monitoring parameters like temperature, humidity, and power usage, WSNs enable us to detect anomalies and inefficiencies as they happen.
Proactive Energy Management:
With WSNs in place, businesses and industries can move beyond reactive approaches to energy management. Real-time monitoring facilitates quick responses to changes, allowing for proactive measures to optimize energy usage and reduce waste.

Cutting the Cord: Wireless Connectivity
Flexibility in Deployment:
Unlike traditional wired systems, WSNs leverage wireless communication protocols, eliminating the need for cumbersome and costly wiring. This flexibility in deployment enables easy sensor placement, making it feasible to cover vast areas and adapt the network as needed.
Scalability:
As industries grow and smart cities evolve, scalability becomes paramount. WSNs rise to the occasion, effortlessly scaling to accommodate a multitude of sensors, ensuring comprehensive coverage without compromising efficiency.
Efficiency at its Core
Low Power Consumption:
WSNs are designed with energy efficiency in mind. Low power consumption ensures that sensors operate for extended periods without draining resources. This characteristic is fundamental to maintaining continuous monitoring without adding an extra burden to energy consumption.
Cost-Effective Operations:
The cost-effectiveness of WSNs is a game-changer. Reduced installation costs, simplified maintenance, and the absence of complex wiring make WSNs an economical choice for businesses aiming to implement energy monitoring systems.

Benefits of Wireless Sensor Networks in Energy Monitoring:
- Real-Time Monitoring:
WSNs enable real-time monitoring of energy consumption, allowing for immediate detection of anomalies and quick response to changes.
- Flexibility and Scalability:
Wireless connectivity allows for flexible sensor placement and easy scalability, making it adaptable to various environments and expanding networks as needed.
- Cost-Effectiveness:
Compared to traditional wired networks, WSNs are often more cost-effective in terms of installation, maintenance, and overall operational expenses.
- Energy Efficiency:
WSNs are designed for low power consumption, ensuring prolonged sensor operation without frequent battery replacements and reducing the overall energy burden.
- Environmental Monitoring:
WSNs can be employed for broader environmental monitoring, contributing to a holistic sustainability approach by measuring factors such as air quality and emissions.
- Quick Deployment:
The wireless nature of WSNs allows for rapid deployment, making it feasible to implement energy monitoring systems in a shorter time frame compared to wired alternatives.
Drawbacks and Challenges of Wireless Sensor Networks in Energy Monitoring:
- Limited Range and Coverage:
The range of wireless sensors may be limited, leading to potential coverage gaps in large or complex environments.
- Interference and Signal Quality:
Wireless signals can be susceptible to interference, affecting signal quality and potentially impacting the accuracy of data transmission.
- Maintenance and Reliability:
While wireless systems simplify installation, they may require more attention to maintenance. Reliability issues, such as sensor malfunctions or connectivity issues, can arise and need prompt resolution.
- Initial Setup Costs:
While WSNs offer long-term cost benefits, the initial setup costs can be relatively high, especially if specialized sensors or infrastructure are required.
- Limited Data Transfer Capacity:
The data transfer capacity of wireless networks may be limited compared to wired alternatives, potentially affecting the speed and volume of data that can be transmitted.
- Power Source Dependency:
Despite efforts to reduce power consumption, WSNs are still dependent on power sources, and if not managed carefully, frequent battery replacements may be necessary, impacting the overall sustainability
Conclusion
Wireless Sensor Networks have emerged as the linchpin of modern energy monitoring, revolutionizing how we approach sustainability. From real-time data insights and wireless connectivity to scalability and efficiency, WSNs are propelling us towards a future where businesses, industries, and cities can optimize energy usage, reduce costs, and contribute to a greener, more sustainable planet. Embracing the power of WSNs is not just a technological choice; it’s a commitment to a better, more energy-efficient world.
Call us on: 9870643534
Mail us at: prashant.yadav@oneunit.in