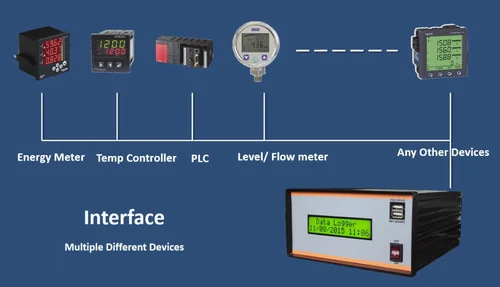
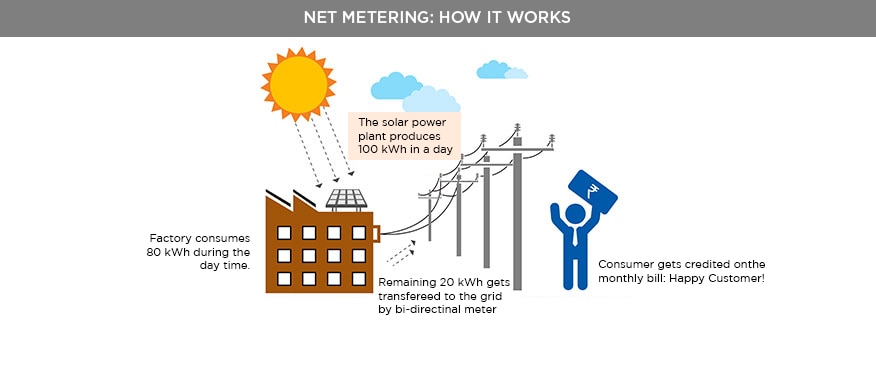
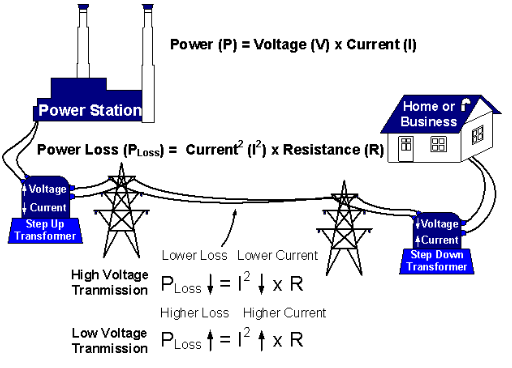
Harnessing the Power of Electrical Data Loggers
In the electrical field, a data logger is a specialized device used to monitor and record various electrical parameters and data over time. These devices play a crucial role in understanding the performance, efficiency, and safety of electrical systems and equipment.